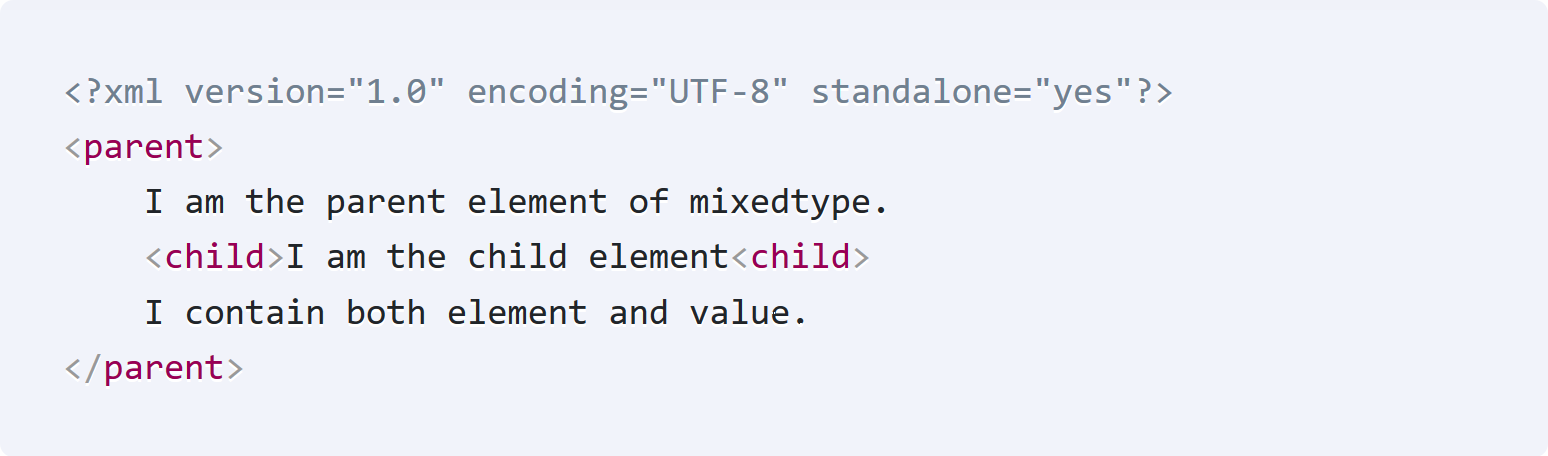
A Mixed type XML element can contain attributes, elements, and text. For example here is an XML element, "parent", that contains both text and an element “child”.
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" standalone="yes"?>
<parent>
I am the parent element of mixedtype.
<child>I am the child element</child>
I contain both element and value.
</parent>So how will we write the Java class for it. You might think of “parent” as @XmlRootElement and
we can get the String inside it by @XmlValue and the child element by @XmlElement.
But this won’t work because @XmlValue and @XmlElement can not be used together.
@XmlValue and @XmlElement can not be used together in JAXB
Parent.java
import java.util.*;
import javax.xml.bind.annotation.*;
@XmlRootElement(name = "parent")
public class Parent{
protected List<Child> child= new ArrayList<>();
protected List<String> text= new ArrayList<>();
@XmlElementRef(name="child",type=Child.class)
public List<Child> getChild() {
return child;
}
@XmlMixed
public List<String> getText() {
return text;
}
public void setChild(Child value) {
this.child.add(value);
}
public void setText(String value) {
this.text.add(value);
}
}So for the root element “parent” we are using @XmlMixed annotation for the texts and
@XmlElementRef for the “child” element. You can think of the use of @XmlMixed similar to
@XmlValue.
Let's take a simple Child class
Child.java
public class Child {
@XmlValue
protected String value;
public String getValue() {
return value;
}
public void setValue(String value) {
this.value = value;
}
}Unmarshalling using JAXBContext:
import javax.xml.bind.JAXBContext;
import javax.xml.bind.Unmarshaller;
JAXBContext jaxbContext = JAXBContext.newInstance(Parent.class);
Unmarshaller jaxbUnmarshaller = jaxbContext.createUnmarshaller();
Parent parent = (Parent) jaxbUnmarshaller.unmarshal(new FileInputStream(xmlFile));Since more than one text content and child element can appear, List<String>
and List<Child> are ONLY allowed for mixed content in JAXB.
We can get all the texts and child elements from the List. Like this:
System.out.println(text.get(0)); // I am the parent element of mixedtype
System.out.println(text.get(1)); // I contain both element and value.