The following guide describes setting up a MySQL Server on ubuntu. We will set up a test database and enable access to connect to it externally using a client. It is not advised to open access to all IP addresses.
If you haven't already installed mysql, installed it with the following command. This guide assumes you are using MySQL 5.7 and above.
sudo apt-get update
sudo apt-get install mysql-server
Accept Yes and complete the installation.
Make sure to open the port 3306.
sudo ufw enable
sudo ufw allow mysqlTo check the status of allowed ports run the following command. sudo ufw status
Next, we want to update the bind-address
ubuntu@server:~$ sudo nano /etc/mysql/mysql.conf.d/mysqld.cnfOn line number 43 with ctrl+ _ (underscore), change the bind-address to allow connection from anywhere
bind-address = 127.0.0.1# Instead of skip-networking the default is now to listen only on
# localhost which is more compatible and is not less secure.
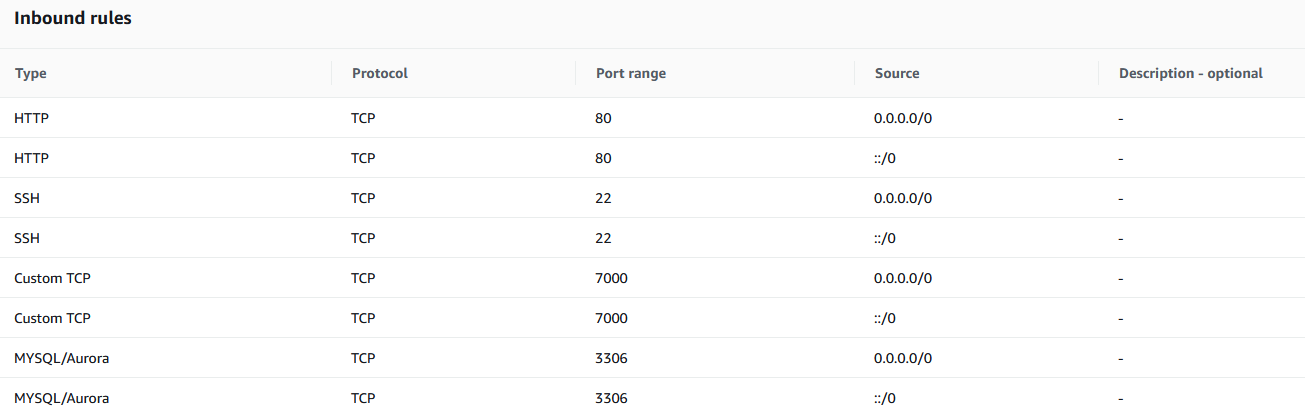
bind-address = 0.0.0.0If you are using AWS Cloud, you need to further enable inbound access to port 3306, apart from ufw
Go to the security group EC2> Security Groups and add MYSQL/Aurora in the inbound rules. Make sure the security group is attached to the EC2 instance where MySQL is installed.
For this purpose, we will create a new user and a database. You can change the name of the db and user as per your need. Avoid using the root user for this purpose
create database deepak;
CREATE USER 'xuser'@'%' IDENTIFIED BY 'password';
GRANT ALL PRIVILEGES ON deepak.* TO 'xuser'@'%';
FLUSH PRIVILEGES;We are also giving access to xuser to access all the tables of deepak from any ip address %
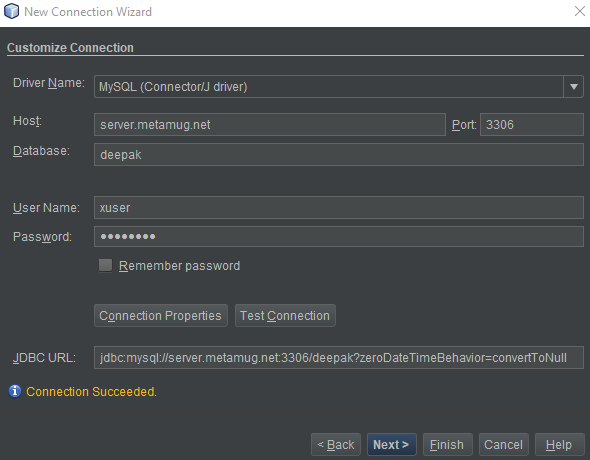
Here we are using Netbeans to connect. Any other database client, workbench or other clients can be used to access the database.

As you can see in the above picture, we have connected to the database. You can check your existing connections with the following command on your ubuntu machine
lsof -i -P | grep :3306